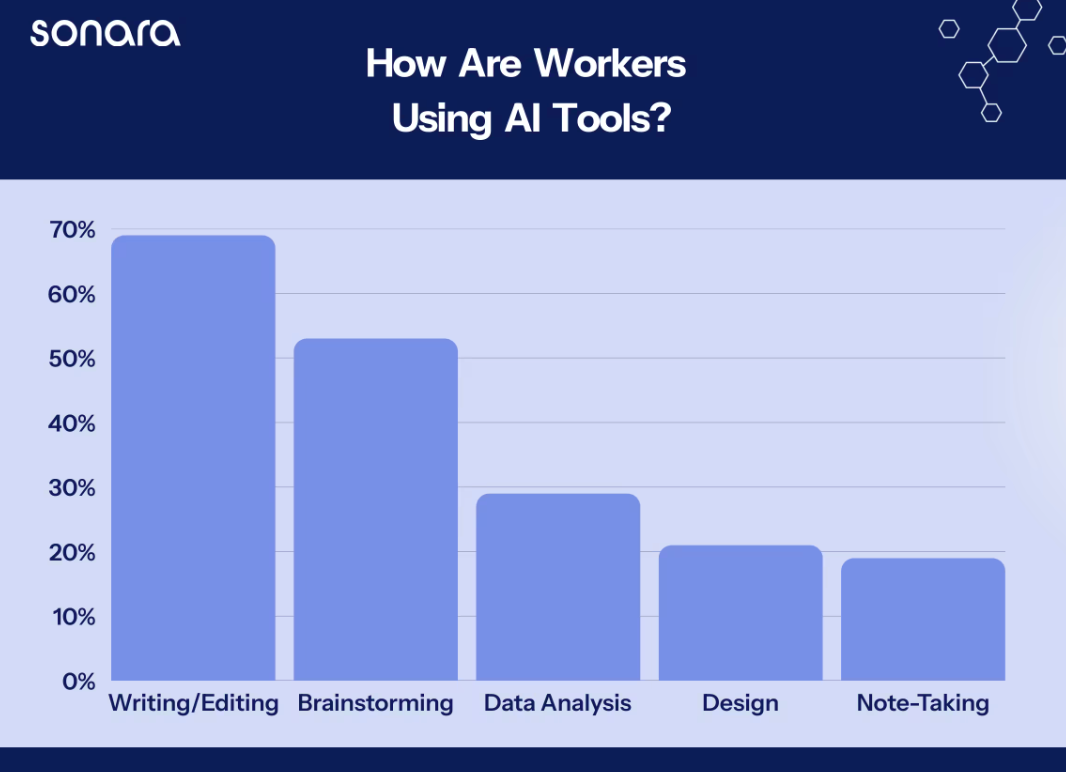
 transparency
transparency
 transparency
transparency
 transparency
transparency
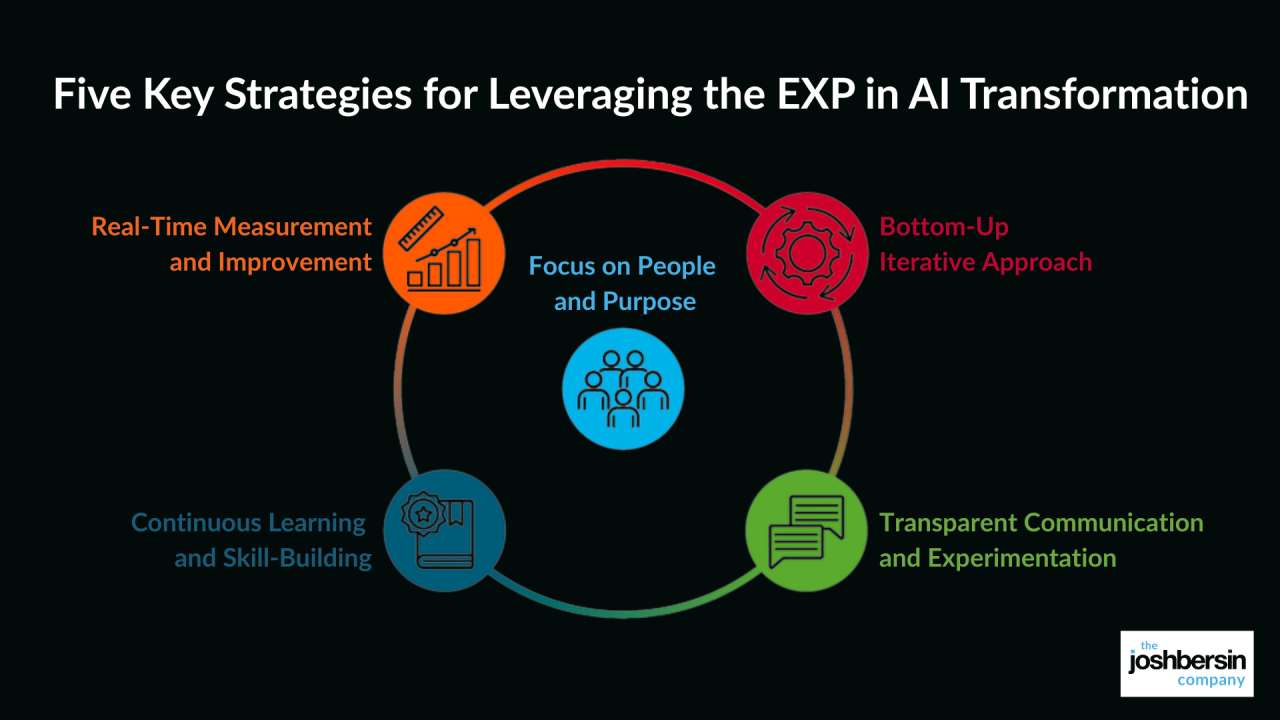 transparency
transparency
 transparency
transparency
 transparency
transparency
 transparency
transparency
 transparency
transparency
 transparency
transparency
 transparency
transparency





 扫一扫
添加客服
扫一扫
添加客服




